Heat Exchanger Fouling and Cleaning VIII – 2009
14-19 June 2009, Schladming, Austria
PREFACE
Heat exchangers play a crucial role in most chemical/petrochemical, food processing and power generating processes. However due to the nature of fluids involved in the process, deposits tend to form on the heat transfer surface which greatly reduce the efficiency of the apparatus. The main purpose of this series of conferences on heat exchanger fouling and cleaning has been to facilitate innovative thinking and to explore new theoretical and practical approaches to address the tremendous challenges associated with fouling of heat exchangers, such as:
- The design of heat exchangers for conditions where severe fouling may be expected
- The inefficient use of primary energy due to fouling, resulting in accelerated depletion of fossil resources and adverse effects on our environment
- Safety and product quality issues related to deposit formation on heat exchanging surfaces
- Reduction of environmentally harmful and potentially hazardous chemical additives
- Efficient monitoring and cleaning tools to offset the impact of fouling,
This series of bi-annual conferences has successfully provided a forum for experts from industry, academia and government research centres from around the world, to present their latest research and technological developments in the areas of fouling mitigation and cleaning technologies. These meetings generally involve overview presentations, technical papers, poster sessions, and panel discussions. Following the meetings organised by Engineering Conferences International in San Luis Obispo, USA (1995), Lucca, Italy (1997), Banff, Canada (1999), Davos, Switzerland (2001), Santa Fé, USA (2003), Kloster Irsee, Germany (2005), Tomar, Portugal (2007), the 8th conference in this series has for the first time been organised under the auspices of EUROTHERM. This conference was held in Schladming, Austria, in June 2009 and provided participants with excellent technical presentations and a very conducive environment for personal discussions. Despite significant financial restrictions world-wide, a record number of 101 participants from 25 countries attended the conference, presenting 81 papers/posters.
The Schladming conference saw many references to the 1983 paper by Prof. Norman Epstein, entitled ‘Thinking about heat transfer fouling: A 5 5 matrix’, [Heat Transfer Engineering, Vol. 4(1): 43-56]. There, Epstein presented an overview of the state of understanding of the five steps (initiation, transport, attachment, removal and ageing) involved in deposit formation for each of the five principal mechanisms of fouling (particulate, chemical reaction, crystallisation, corrosion and bio-fouling). Given that 25 years had passed since the concept was introduced, the organisers through Dr Ian Wilson, who collated and analysed the data, asked the delegates at the conference – as a representative sample of those active in fouling and cleaning research worldwide – to express their view of the current state of understanding. This was performed by means of a questionnaire, where respondents were asked to indicate their level of experience in their assessment as either (A) expert, (B) experienced, or (C) less confident. The scale of understanding was set as ranging from 1 (little or no understanding) to 5 (understanding well developed).
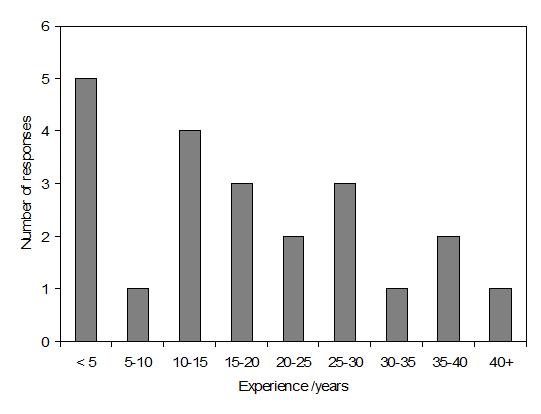
22 responses were received, some of which were submitted by groups. Respondents were also asked to indicate how long they had been working on fouling and cleaning, this information is provided in Figure 1.
The distribution of expertise in Table 1 indicates a relatively low level of expertise in the areas of biofouling and, to a certain extent, corrosion fouling. This reflected the coverage of these topics in the conference papers. The biofouling area, in particular, was noted as one where a parallel community exists, with dedicated journals and conferences.
Table 1 Respondent’s level of expertise in each fouling mechanism (in %). Sample population 22: not all respondents submitted assessments for each mechanism.
| Mechanism | # | Expert | Experienced | Less confident |
| Biofouling | 19 | 9 | 27 | 63 |
| Particulate | 19 | 17 | 63 | 19 |
| Chemical reaction | 18 | 20 | 54 | 26 |
| Crystallisation | 18 | 27 | 46 | 28 |
| Corrosion | 18 | 21 | 44 | 34 |

The noteworthy points are the presence of several of high scores, particularly in crystallisation fouling, and the paucity of low scores (< 2), with the exception of ageing, indicating that progress has been made. Interestingly, ageing was identified as the topic having received least attention in the 1983 paper. The general lesson appears to be that there is still work to be done, as the award of ‘5’ indicated that the topic was well understood, managed in practice or reliable software available to guide mitigation. One respondent commented on the fact that the matrix only considers each fouling mechanisms in isolation – if fouling caused by combinations of mechanisms is taken into consideration as well, then there is a whole ‘Rubik’s Cube’ waiting to be tackled!
The following papers have been presented at the Schladming conference and have been recommended for publication in the final conference e-proceedings after a careful refereeing and revision process. The e-proceedings cover various aspects of heat exchanger fouling along with updated state-of-art fouling mitigation and cleaning strategies. The present e-proceedings as well as those from the previous conferences since 2003 can be obtained free of charge on the above internet homepage.
The editors wish to thank everybody who contributed to the conference and the conference proceedings, i.e.
- all the authors and participants who invested substantial efforts to produce high-quality papers and to attend the conference
- the technical referees who helped to improve the quality of these papers even further, by providing valuable and helpful comments
- the Conference Advisory Committee and the Session Chairmen
- Mrs Elham Key Manesh and Mrs Renate Steinhagen, for the preparation and finalisation of the program, the compilation of the final proceedings and maintenance of the conference homepage.
Editors
Hans Müller-Steinhagen
German Aerospace Centre and University of Stuttgart (Germany)
M. Reza Malayeri
University of Stuttgart (Germany)
A. Paul Watkinson
University of British Columbia (Canada)
Guest editor for the preface
Ian Wilson
University of Cambridge
ARTICLES
(PDF documents)
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- FOULING IN CRUDE OIL
PREHEAT TRAINS: A SYSTEMATIC SOLUTION TO AN OLD PROBLEM
S. Macchietto, G.F. Hewitt, F. Coletti, B.D. Crittenden, D.R. Dugwell1, A. Galindo, G. Jackson, R. Kandiyoti, S.G.Kazarian, P.F. Luckham, O.K. Matar, M. Millan-Agorio, E.A. Müller, W. Paterson, S.J. Pugh, S.M. Richardson and D.I. Wilson - RELATE CRUDE OIL
FOULING RESEARCH TO FIELD FOULING OBSERVATIONS
H. M. Joshi, N. B. Shilpi, and A. Agarwal - CHARACTERISATION OF
CRUDE OILS AND THEIR FOULING DEPOSITS USING A BATCH STIRRED CELL SYSTEM
Andrew Young, Silvia Venditti, Cesur Berrueco, Mengyan Yang, Andrew Waters, Haddy Davies, Simon Hill, Marcos Millan and Barry Crittenden - FOULING CHARACTERISTICS
OF A HEAVY VACUUM GAS OIL IN THE PRESENCE OF DISSOLVED OXYGEN
A.P. Watkinson and Y-H. Li - FOULING: IMPLEMENTATION
OF A CRUDE PREHEAT TRAIN PERFORMANCE MONITORING APPLICATION AT THE IRVING OIL
REFINERY
A.J. Waters, C.G. Akinradewo, D. Lamb - EXPERIENCE IN THE
APPLICATION OF COMPABLOC™ IN REFINERY PRE-HEAT TRAINS AND FIRST ANALYSIS OF DATA FROM AN OPERATIONAL
UNIT
E. Andersson, J. Quah and G.T. Polley - DEVELOPING
CHARACTERISATION METHODS FOR FOULANTS DEPOSITED IN REFINERY HEAT EXCHANGERS
S. Venditti, C. Berrueco, P. Alvarez, T. J. Morgan, M. Millan, A.A. Herod and R. Kandiyoti - THE IMPORTANCE OF
SCHEDULING AND DESALTER CONTROL OF PREHEAT TRAINS OF CRUDE DISTILLATION UNITS: A CASE
STUDY
E.M. Ishiyama, D.I. Wilson, W.R. Paterson, A. V. Heins and L. Spinelli - REFINERY PRE-HEAT TRAIN
NETWORK SIMULATION UNDERGOING FOULING: ASSESSMENT OF ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND CARBON
EMISSIONS
F. Coletti and S. Macchietto - MODELLING THE FOULING
INDUCTION PERIOD
Mengyan Yang, Andrew Young, Amir Niyetkaliyev and Barry Crittenden - KINETICS AND STRUCTURAL
EVOLUTION DURING AGING OF COKER VAPOUR DEPOSITS
Z. Fan and A. P. Watkinson - DEPOSITION OF SOLIDS
FROM A PETROLEUM HEPTANE-SOLUBLE FRACTION UPON HEATING IN A MICRO-BOMB REACTOR
S. Venditti, C. Berrueco, P. Alvarez, T.J. Morgan, M. Millan, A.A. Herod and R. Kandiyoti - THE INVESTIGATION OF
PARTICULATE CORROSION PRODUCT DEPOSITION ON HEAT TRANSFER SURFACES: A COMPARISON OF EXPERIMENTS AND
THEORY AND A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF THE REMOVAL MECHANISM
K. Khumsa-ang and D. H. Lister - ASSESSMENT OF ASH
FOULING AND SLAGGING IN COAL FIRED UTILITY BOILERS
Jan Taler, Marcin Trojan and Dawid Taler - PREDICTION OF THE
SLAGGING STATE ON COAL-FIRED BOILERS BASED ON VAGUE SETS
Xu Zhi-ming, Wen Xiao-qiang, Zhang Ai-ping, Sun Yuan-yuan, Sun Ling-fang - CALCULATION OF HAMAKER
CONSTANTS APPLIED TO THE DEPOSITION OF METALLIC OXIDE PARTICLES AT HIGH TEMPERATURE
G. Lefèvre and A. Jolivet - FOULING PROBLEMS IN
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION COOLERS IN THE AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY
M.S. Abd-Elhady, M.R. Malayeri and H. Müller-Steinhagen - DEPOSIT FORMATION IN
EVAPORATION OF A PULP MILL EFFLUENT
Yonghua Li and A. Paul Watkinson - SCALE FORMATION IN
SYNTHETIC BAYER LIQUOR FOLLOWED BY QUARTZ CRYSTAL MICROBALANCE
F. Brisach, A. Brisach-Wittmeyer, N. Amokrane, N. A. Bouchard, H. Menard, and A. Lasia - ADSORPTION MEASUREMENT
OF SCALE INHIBITORS ON STEEL IN BAYER PROCESS
E. St-Jean, O. Savary, A. Brisach-Wittmeyer, H. Ménard N.A. Bouchard and R. Breault - APPLICATION OF
ANTIFOULING SURFACES IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER FOR FOOD PRODUCTION
A. Bani Kananeh, E. Scharnbeck and D. Hartmann - IMPROVING CLEANING OF
INDUSTRIAL HEAT INDUCED FOOD AND BEVERAGES DEPOSITS: A SCIENTIFIC APPROACH TO
PRACTICE.
K. Asteriadou, A.M. Othman, K. Goode and P.J. Fryer - EFFECT
OF SEASONAL VARIATION IN MILK COMPOSITION ON DAIRY FOULING
B. Bansal, B. Habib, H. Rebmann and X. D. Chen - REMOVAL FORCE
MEASUREMENT AND RHEOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF SWEETENED CONDENSED MILK DEPOSITS: A PRELIMINARY
STUDY
A.M. Othman, K. Asteriadou and P.J. Fryer - EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS
OF THE EFFECTS OF PARTICULATE FOULING ON HEAT EXCHANGER HEAT TRANSFER AND AIR SIDE PRESSURE DROP FOR A
HYBRID DRY COOLER
I.H. Bell, E.A. Groll and H. König and T. Odrich - PRELIMINARY STUDY OF
PARTICULATE FOULING IN A HIGH TEMPERATURE CONTROLLED EXPERIMENTAL FACILITY
K. K. Sathyanarayanarao Subbarao, C. C. M Rindt and A. A. van Steenhoven - EVALUATION OF OLIGOMER
FOULING RESISTANCE IN A PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER FOR HEAT RECOVERY FROM POLYESTER DYEING
WASTEWATER
A. Gavin, G. Rovero and N. Epstein - FOULING IN HIGH SOLID
CONTENT SUSPENSION-EFFECT OF NUCLEATING AIR AND BACKGROUND ELECTROLYTE
M. Riihimäki, U. Ojaniemi, T. J. H. Pättikangas, T. M. Pääkkönen, M. Manninen, E. Puhakka, E. Muurinen, C. J. Simonson, R. L. Keiski - INFLUENCE OF THE APEX
ANGLE OF CONE SHAPED TUBES ON PARTICULATE FOULING OF HEAT EXCHANGERS
M.S. Abd-Elhady, C.C.M. Rindt and A.A. van Steenhoven - CRYSTALLIZATION FOULING
OF CaCO3 – EFFECT OF BULK PRECIPITATION ON MASS DEPOSITION ON THE HEAT TRANSFER
SURFACE
T.M. Pääkkönen, M. Riihimäki, E. Puhakka, E. Muurinen, C.J. Simonson and R.L. Keiski - CONSIDERATION OF
DYNAMIC UNCERTAINTY IN FOULING EXPERIMENTATION
A. Al-Janabi, M. Esawy, M.R. Malayeri and H. Müller-Steinhagen - AGEING: LOOKING BACK
AND LOOKING FORWARD
D.I. Wilson, E.M. Ishiyama, W.R. Paterson and A.P. Watkinson - PREDICTION OF FOULING
THICKNESS AND BULK MILK OUTLET TEMPERATURE BY ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK (ANN) MODELING IN HELICAL TRIPLE
TUBE MILK STERILIZERS
A. Chaturvedi, S. Acharya and A. K. Datta - DEPOSITION MODELING
FROM MULTI-PHASE DISPERSED FLOW – A BOUNDARY LAYER WALL FUNCTION APPROACH
S.G. Johnsen and S.T. Johansen - MATHEMATICAL MODELLING
OF ASPHALTENES DEPOSITION AND REMOVAL IN CRUDE DISTILLATION UNITS
D. Sileri, K. Sahu, H. Ding and O.K. Matar - DFT STUDIES ON THE
FORMATION OF CaCO3 DEPOSITIONS ONTO CRISTOBALITE, DIAMOND AND TITANIUM CARBIDE
SURFACES
E. Puhakka, M. Riihimäki, T.M. Pääkkönen and R.L. Keiski - CONSTRUCTION OF HIGH
PREDICTIVE FOULING MODELS USING STATISTICAL METHODS
Hiromasa Kaneko, Susumu Inasawa, Hirofumi Inokuchi, Kimito Funatsu - EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD
STUDIES OF FAT FOULING IN A NOVEL SPINNING DISC SYSTEM
R.Y. Nigo, Y.M.J. Chew, N.E. Houghton, W.R. Paterson and D.I. Wilson - USE OF CFD TO CORRELATE
CRUDE OIL FOULING AGAINST SURFACE TEMPERATURE AND SURFACE SHEAR STRESS IN A STIRRED FOULING
APPARATUS
Mengyan Yang, Andrew Young and Barry Crittenden - ANTIFOULING AND
ANTICORROSION PROPERTIES ON SURFACES OF TiO2 NANOMETER FILMS COATED WITH LIQUID PHASE
DEPOSITION
L.L. Wang, M.Y. Liu - MINIMIZATION OF CaSO4
DEPOSITION THROUGH SURFACE MODIFICATION
A. Al-Janabi, M.R. Malayeri and H. Müller-Steinhagen - DEVELOPMENT AND
EVALUATION OF MODIFIED DLC COATINGS TO MINIMIZE PSEUDOMONAS FLUORESCENS ADHESION
Q. Zhao, X.J. Su, S. Wang, X.L. Zhang, P. Navabpour and D. Teer - ENHANCEMENT OF HEAT
TRANSFER IN CRYSTALLIZATION FOULING DUE TO SURFACE ROUGHNESS
F. Albert, W. Augustin and S. Scholl - CRYSTALLIZATION FOULING
OF FINNED TUBES DURING POOL BOILING: EFFECT OF FIN DENSITY
M. Esawy, M.R. Malayeri and H. Müller-Steinhagen - INFLUENCE OF SURFACE
DEFECTS AND AGING OF COATED SURFACES ON FOULING BEHAVIOR
T. Geddert, W. Augustin and S. Scholl - Biocorrosion induced by
Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on Stainless Steel – A Preliminary Study
H. Men, C.H. Wang, Y. Peng, S.R. Yang and Z.M. Xu - PRECIPITATION FOULING
ON VARIOUS AUSTENITIC ALLOYS
A. Al-Janabi, M.R. Malayeri, H. Müller-Steinhagen and O.O. Badran - RISK-BASED DESIGN
MARGIN SELECTION FOR HEAT EXCHANGERS
R.L. Shilling, M.P. Rudy, and T.M. Rudy - DESIGN OF
SHELL-AND-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS TO ACHIEVE A SPECIFIED OPERATING PERIOD IN REFINERY PRE-HEAT
TRAINS
G.T. Polley, A. Morales Fuentes & S.J. Pugh - REVAMPING EXISTING
SEVERELY FOULING CONVENTIONAL HEAT EXCHANGERS INTO A SELF-CLEANING (FLUIDISED BED) CONFIGURATION: NEW
DEVELOPMENTS AND EXAMPLES OF REVAMPS
D.G. Klaren and E.F. de Boer - PROCEDURE FOR APPLYING
FOULING MODELS TO PREDICT OVERALL FOULING RATES IN INDUSTRIAL HEAT EXCHANGERS
G.T. Polley, G. Gonzales-Garcia - FOULING AND FOULING
MITIGATION ON DIFFERENT HEAT EXCHANGING SURFACES
S. N. Kazi, G. G. Duffy and X. D. Chen - CONTROL OF BIOFOULING
OF INDUSTRIAL SURFACES USING MICROPARTICLES CARRYING A BIOCIDE
Ferreira C., Simões M., Pereira M.C., Bastos M.M.S.M., Nunes O.C., Coelho M. and Melo L.F. - MITIGATION OF CALCIUM
CARBONATE FOULING USING RF ELECTRIC FIELDS
L.D. Tijing, H.Y. Kim, D.H. Lee, C.S. Kim and Y.I. Cho - PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
OF A ZERO-FOULING RECIPROCATING SCRAPED SURFACE HEAT EXCHANGER
J.P. Solano, A. García, P.G. Vicente and A. Viedma - HEAT EXCHANGER
PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT THROUGH THE USE OF TUBE INSERTS IN REFINERIES AND CHEMICAL PLANTS – SUCCESSFUL
APPLICATIONS: SPIRELF®, TURBOTAL® AND FIXOTAL® SYSTEMS
A. Krueger and F. Pouponnot - EXPERIMENTAL
INVESTIGATION OF TURBULENCE LEVEL IN ENHANCED EXCHANGERS WITH ACTIVE INSERT DEVICES
D. Crespí, P.G. Vicente, J.P. Solano, A. García and A. Viedma - Solving Heat Exchanger
Tube Problems with Thin Film Thermally Conductive Coating Applications and Novel Tube and Pipe Cleaning
as a Precursor to Coating Application and NDT
E.L. Curran - INVESTIGATING THE
REMOVAL OF DISSOLVED INORGANIC ELEMENTS FROM A GAS CONDENSATE STREAM AT SECUNDA SASOL SYNFUELS USING
ALUMINA IN CONTINUOUS MODE
Ratale H. Matjie , Jeeten. Nathoo , N. Mbedzi and Alison E. Lewis - FOULING AND CLEANING
MONITORING USING THE MSS – INDUSTRIAL PERSPECTIVE
A. Pereira, L.F.Melo, J. Martins and M. Freire - HEAT EXCHANGER CLEANING
USING ICE PIGGING
E.A. Ainslie, G.L. Quarini, D.G. Ash, T.J. Deans, M. Herbert and T.D.L. Rhys - LINEAR
PARAMETER-VARYING IDENTIFICATION OF A CROSS FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER FOR FOULING DETECTION: A PRELIMARY
STUDY
G. Mercère, H. Pálsson and T. Poinot - FOULING DETECTION IN A
CROSS-FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER BASED ON PHYSICAL MODELING
O. Gudmundsson, O.P. Palsson, H. Palsson and S. Lalot - MONITORING OF THE LOCAL
CLEANING EFFICIENCY OF PULSED FLOW CLEANING PROCEDURES
Martin Schöler, Tatjana Fuchs, Manuel Helbig, Wolfgang Augustin, Stephan Scholl and Jens-Peter Majschak - QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION
OF FOULING UNDER A WELL-DEFINED SHEAR FLOW
S. Inasawa, M. Mukai, N. Morimoto, M. Nakamura, H. Inokuchi and Y. Yamaguchi - FLUID DYNAMIC GAUGING
APPLIED TO ANNULAR TEST APPARATUSES FOR FOULING AND CLEANING
T. Gu, F. Albert, W. Augustin, Y.M.J. Chew, W.R. Paterson, S. Scholl, I. Sheikh, K. Wang, D.I. Wilson - DEVELOPMENT OF THE
SCANNING FLUID DYNAMIC GAUGE
P.W. Gordon, Y.M.J. Chew and D.I. Wilson - DETECTION OF FOULING IN
A CROSS-FLOW HEAT EXCHANGER USING WAVELETS
H. Ingimundardóttir and S. Lalot
